Virtual Sensing
虛擬傳感活動自 2012 年以來一直沿著這些方向開展
薄膜形狀和負載傳感
與俄勒岡州立大學合作。
這項活動是與俄勒岡州立大學的一個團隊(由 Roberto Albertani 教授領導)合作進行的,根據空軍科學研究辦公室 (AFOSR) 的合同,“實時機翼渦流和壓力分佈估計機翼在不穩定和過渡飛行條件下的位移和應變”,2012-2016 年,Gregg Abate 博士擔任技術監測員。
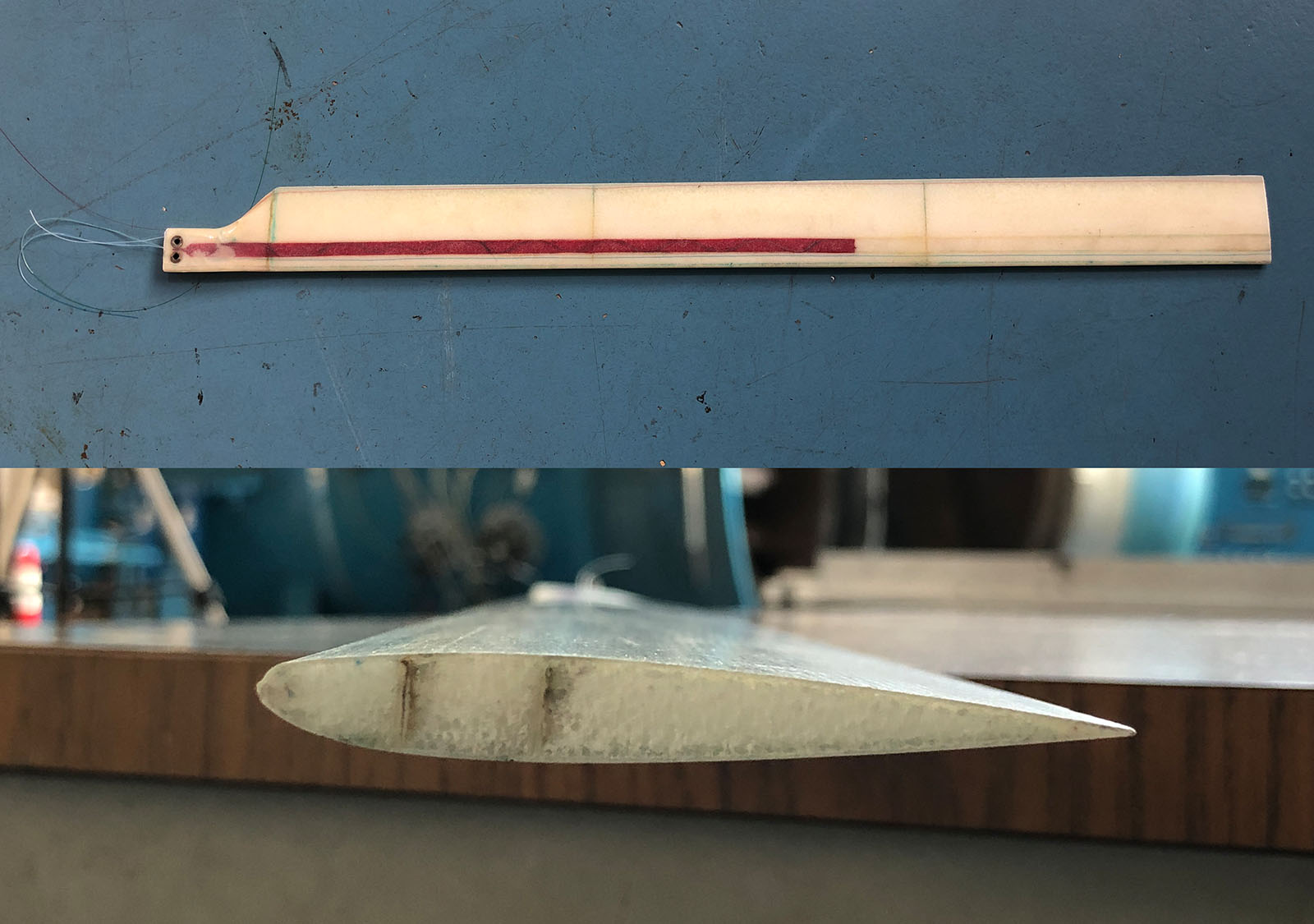
已經開發了一種新的公式來重建膜的形狀,以及施加在膜上的壓力載荷,從分佈應變測量。該方法已通過與從代表微型飛行器的樣本中獲取的靜態和動態測量值的相關性得到驗證,使用數字圖像相關性 (DIC) 進行應變和位移(後者用於驗證)。

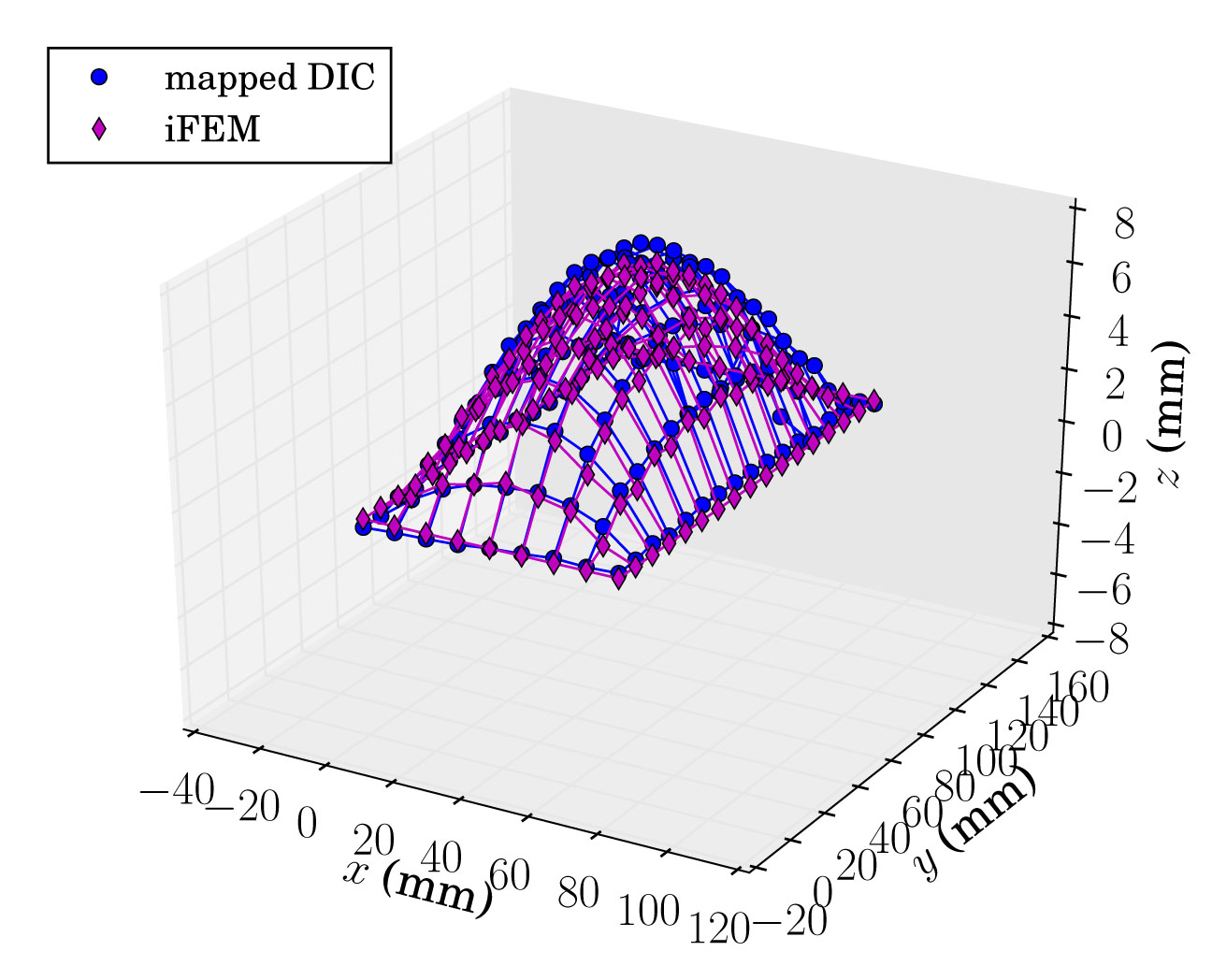
重點產品
- M. Alioli, P. Masarati, M. Morandini, R. Albertani, T. Carpenter,“薄膜張力對薄膜機翼動態失速的建模效果”,航空航天科學與技術,69:419-431,2017 年 10 月,doi :10.1016/j.ast.2017.07.008。
- M. Alioli、P. Masarati、M. Morandini、T. Carpenter、NB Osterberg、R. Albertani,“使用逆有限元分析進行膜形狀和橫向載荷重建”,AIAA 期刊,55(1):97-308,2017 ,doi:10.2514/1.J055123。
該活動促成了米蘭理工大學的 Mattia Alioli 以及俄勒岡州立大學的 Trenton Carpenter 和 Brent Osterberg 博士畢業。
轉子葉片形狀和載荷重建
這項活動是與羅馬特雷大學(Giovanni Bernardini 和 Jacopo Serafini)的一個團隊合作發起的,目前正在繼續,合作一個由法蘭德斯創新與創業 (VLAIO) 機構資助並由 Siemens Digital Industries Software (Tommaso Tamarozzi) 領導的項目和 KU Leuven (Wim Desmet)。
該活動導致羅伯托·波切利 (Roberto Porcelli) 在羅馬特雷 (Roma Tre) 畢業。
Roberta Cumbo 是 KU Leuven 的博士研究員,也是米蘭理工大學的訪問博士,目前正在從事該項目。
刀片感應
與羅馬三大學合作
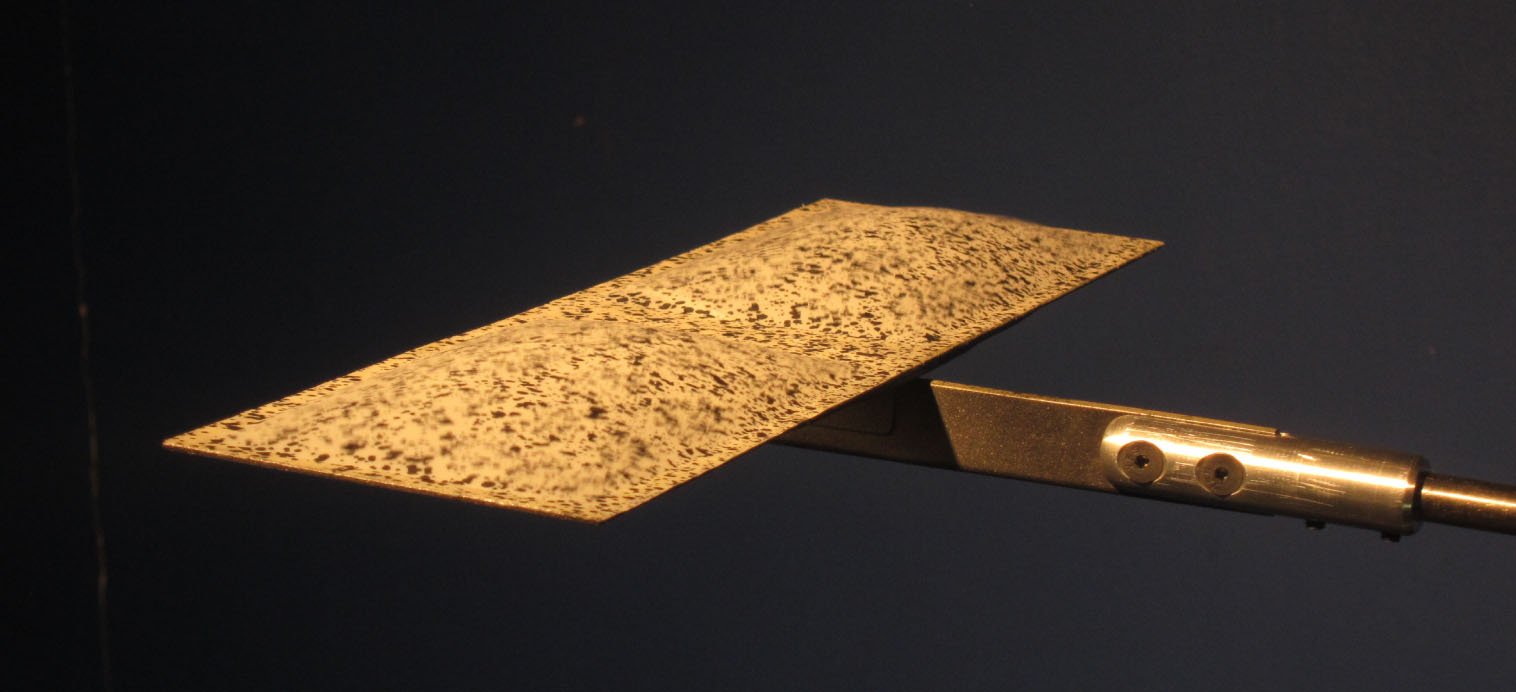
這項活動產生了一種新的方法來重建承受大彎曲和扭轉應變的樑的形狀,這特別適用於承受大空氣動力和離心載荷的旋翼飛機葉片。該方法已通過基於免費通用求解器 MBDyn 的非線性多體動力學獲得的模擬應變測量得到驗證。可預見在轉子狀態重建和結構健康監測中的應用。未來的發展將看到與其他傳感器類型的進一步集成。
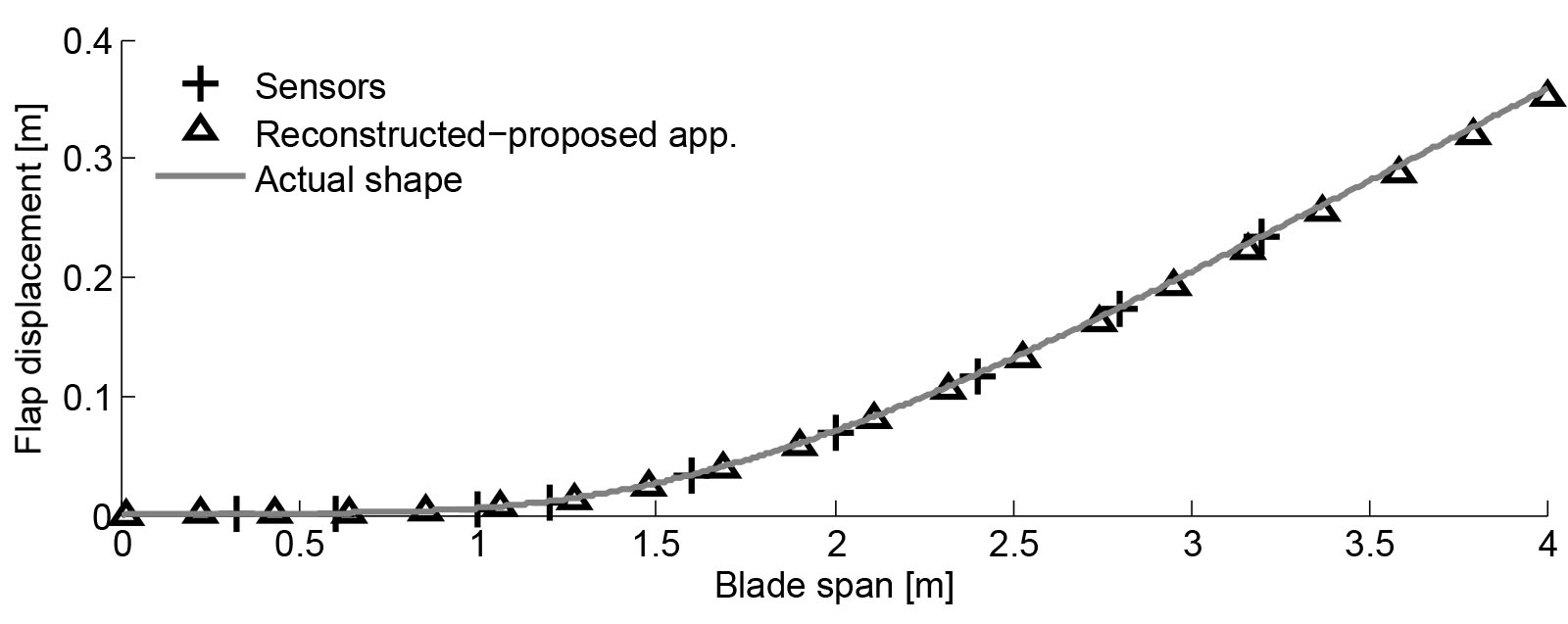
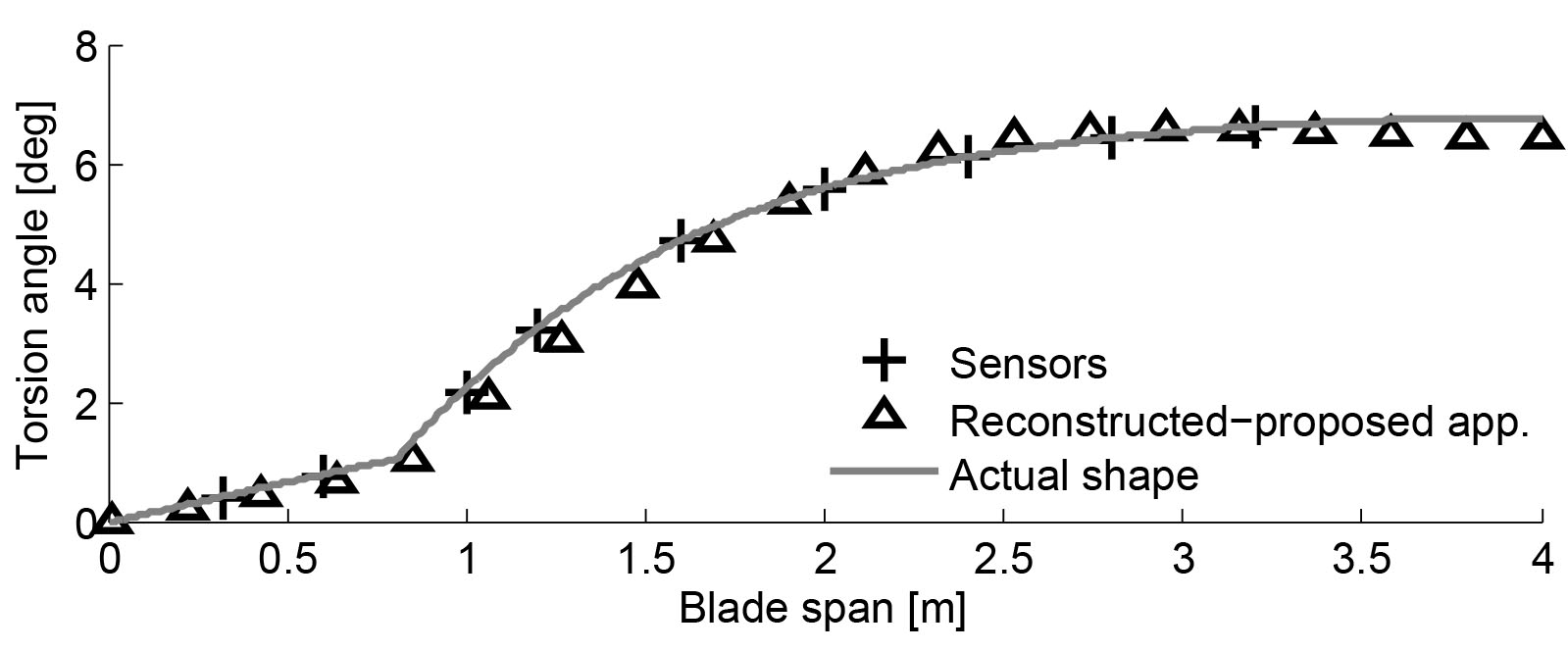
重點產品
- J. Serafini, G. Bernardini, R. Porcelli, P. Masarati, "In-Flight Health Monitoring of Helicopter Blades via Differential Analysis", Aerospace Science and Technology, 88:436-443, 2019, doi:10.1016/j.ast.2019.03.039.
- G. Bernardini, R. Porcelli, J. Serafini, P. Masarati, "Rotor Blade Shape Reconstruction from Strain Measurements", Aerospace Science and Technology, 79:580-587, August 2018, doi:10.1016/j.ast.2018.06.012.
SINCRO: A general strategy for load and parameter identification for helicopter main rotor systems
In cooperation with Siemens Digital Industries Software, KU Leuven, VLAIO - Vlaanderen Agentschap Innoveren & Ondernemen, Airbus Helicopters.

SINCRO is a PhD project funded by the Flanders Innovation and Entrepreneurship (VLAIO) agency. This project addresses the problem of load and parameter identification for helicopter-related applications. The proposed solution is the use of a Virtual and Augmented Sensing strategy which estimates unmeasured quantities (e.g. loads, full-field strains, displacements and accelerations) by readily combining experimental and numerical data of the analyzed system. In particular, a Kalman-based methodology will be investigated and further developed with the aim to advance the state-of-the-art of this technique and explore its performance and feasibility for helicopter rotor applications. To this end, the applicability of the proposed strategies will be tested on three industrial case scenarios:
i) design phase of the helicopter,
ii) flight-test (validation and qualification),
iii) operation (system monitoring).
The final goal of this research project is to offer a potential industrial tool for the system identification problem improving the methodologies currently adopted from aerospace companies.
A specimen is currently being produced for benchmarking of the developed methods. It consists of a model scale helicopter rotor blade, instrumented with an innovative sensor based on fiber optics and capable to measure axial and shear strains at selected locations along the blade span. The model and the experimental results will be made available as an open dataset for independent benchmarking.
Key Products
- R. Cumbo、T. Tamarozzi、W. Desmet、P. Masarati,“通過基於卡爾曼的方法對旋轉直升機葉片進行狀態和力估計”,Sensors 2020, 20(15), 4196, doi: 10.3390/s20154196。
